Synchronizing Local Files
Users can create and manage unlimited agents using local ES5 JavaScript files (the Agent’s script). These can be tracked and synced with a running Kubeshark instance using the CLI.
Prerequisites
Install the kubeshark CLI using a method from the installation guide.
Assume a file named anomaly-agent.js is located at:
/Users/me/agents/anomaly-agent.jsTrack All Files in a Folder
kubeshark scripts --set scripting.source=/Users/me/agents/Track Individual Files
kubeshark scripts --set scripting.sources[0]=/Users/me/agents/anomaly-agent.js Any change to a tracked file will be synchronized with the running Kubeshark instance. Adding a new file or deleting an existing one is also treated as a change and will be synced with the deployed Kubeshark instance.
Determining the Agent Name
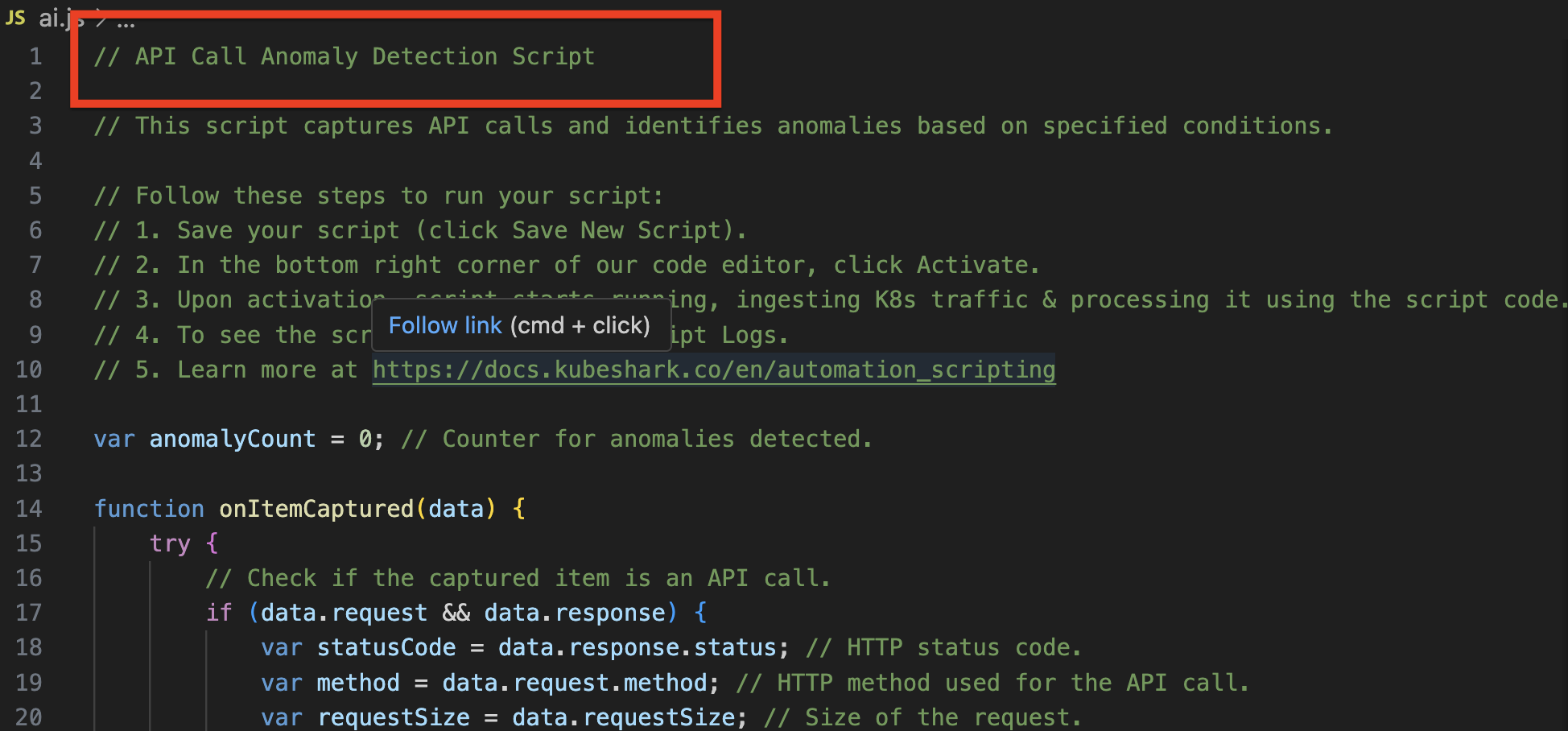
The CLI extracts the agent name from the first line of the Agent’s script (as a comment).
Example name: API Call Anomaly Detection Script
Environment Variables
Agent scripts can access environment variables set in the configuration.
Example:
scripting:
env:
ZAP_SERVER_URL: https://a6a4...-free.app
ZAP_APIKEY: shshh
AWS_REGION: us-east-1
S3_BUCKET: vol-ks...d-demo
# AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: "AK...N"
# AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: "xZ...ie"
KINESIS_STREAM_NAME: "stream1"
KINESIS_MIN_BATCH_SIZE: "10"