Proof of Concept (POC) Checklist
Contact-us to start your POC now.
Kubeshark is pleased to offer POC licenses to qualifying users. The goal of the POC is to validate that Kubeshark operates effectively within the user’s environment, can process specific workloads, and provides a tangible, hands-on experience.
POC Goals
- Verify compatibility with cluster environments (e.g., EKS, OpenShift, Tanzu), CNIs, etc.
- Confirm that Kubeshark can process the user’s workloads
- Evaluate resource consumption
- Validate core functionality
- Gain hands-on experience with some of Kubeshark’s advanced features
POC Steps
Installing Kubeshark should take only a few minutes. The following sequence of steps is recommended to achieve the goals outlined above. It is important to follow the order and ensure each step is completed before proceeding to the next.
- Set up a Slack channel and schedule the two POC meetings
- Select a POC cluster
- Identify POC workloads
- Self-deploy and verify traffic visibility
- Apply the POC configuration, including the license
- Re-install and activate Kubeshark from dormant mode and verify workload visibility
- Confirm stability of all components (e.g., Workers, Hub, Front), resource usage, and log cleanliness
- Explore advanced features
1. Schedule
The POC timeframe typically spans 2–3 weeks and can be extended if needed. To begin, two meetings should be scheduled approximately one week apart:
-
Installation and Basic Usage Verification The user should complete steps 1–3 before this meeting. Steps 4–6 will be covered during the session.
-
Advanced Features Walkthrough This meeting will focus on step 8, tailored to the user’s specific areas of interest.
Before starting the POC, make sure these two meetings are added to the calendar.
2. Selecting the POC Cluster
Choose a cluster to run the POC. The selected cluster should not be a production environment. Production deployment can be considered after successful validation.
The cluster should meet the following requirements:
- Resource allocation below 70%
- Fewer than 20 nodes
- Not under heavy load
3. Identifying the POC Workloads
Workloads must be user-owned and not third-party or default Kubernetes services. Preferably, these are in-house applications or workloads deployed specifically for the POC. Users should be familiar with and able to validate these workloads.
4. Preliminary Installation
Follow the installation instructions to install Kubeshark. No further installation is required. Running Kubeshark without a license enables processing of up to 10,000 API calls, allowing compatibility validation before applying the POC license.
To unlock full POC capabilities, apply the configuration in the next step.
5. POC Configuration
Include the following configuration in your values.yaml file for Helm installation:
tap:
stopped: true # Start Kubeshark in dormant state
regex: <pod-regex> # Regex or prefix to identify the POC workloads (e.g. `(pod1|pod2)`)
namespaces:
- <namespace-name-1> # Namespace filters to target relevant workloads
- <namespace-name-2>
license: <your-poc-license>6. Re-install & Verify
Re-install Kubeshark with the updated POC configuration and perform the following validations:
6.1. Activate
Kubeshark will start in dormant mode with minimal resource usage.
Activate it by pressing the red button. It should turn green.
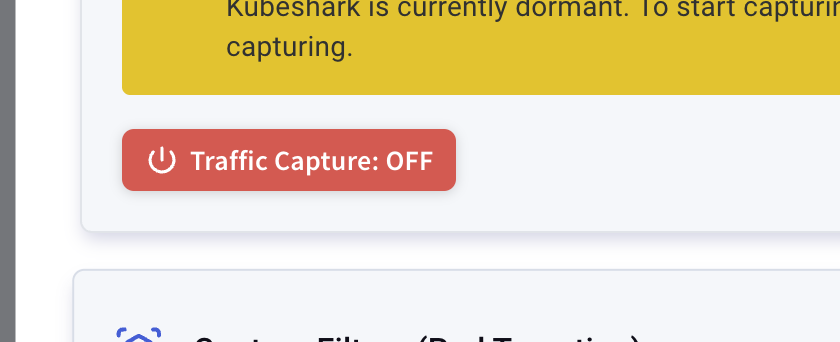
6.2. Verify POC Workloads
Once activated, your POC workloads should be visible. Switch between the API log stream and the service map to validate visibility.
7. Verify Functionality, Resources and Log Messages
7.1. OPTIONAL: Verify eBPF Functionality
If API calls are visible, check for this logo:
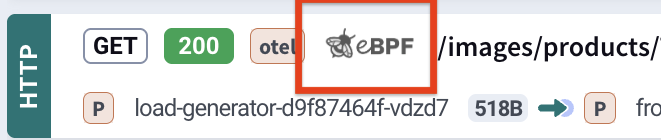 Its presence confirms eBPF is functioning correctly.
Its presence confirms eBPF is functioning correctly.
If this logo appears instead, eBPF is not functioning properly:
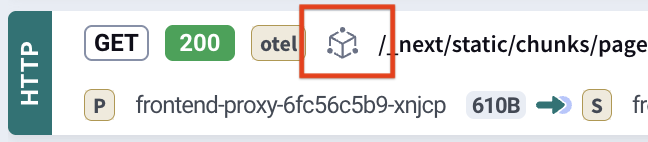
If both appear, your cluster likely has mixed eBPF support across nodes.
7.2. Resources and Logs
Ensure CPU and memory usage are within acceptable limits. Confirm that all components (Workers, Hub, Front) are running stably with no restarts or recurring error logs.
8. Advanced Features
In the second meeting, we’ll walk through advanced features based on your goals and interest. Suggested topics include:
- Smart traffic recording
- Take a historical traffic snapshot (PCAP)
- Generating custom reports
- Network Agents (Traffic monitoring)
- Integrations (e.g., with Grafana)