Packet Capture Options
Kubeshark supports numerous packet capture options catering to a wide range of kernel versions and available capabilities. Each option has its own pros and cons. Having a variety of options to choose from guarantees traffic capture is performant and robust.
eBPF
How to Use: --set packetCapture=ebpf
While eBPF is the most modern packet capture option and the one we recommend using, it has some limitations.
Pros: Performant, robust information (e.g. superior pod-name/IP resolution), taps both the network interface, the kernel OS, and XDP.
Cons: Supported from kernel version 5.0 and up. Requires elevated security capabilities.
The eBPF option requires the following security capabilities:
- SYS_ADMIN
- SYS_PTRACE
- SYS_RESOURCE
- IPC_LOCK
The eBPF packet capture option is different from the eBPF-based TLS packet capture.
AF_PACKET
Kubeshark uses AF_PACKET as the default packet capture option.
To set explicitly, use: --set packetCapture=af_packet.
AF_PACKET operates at the network interface level. It is a mature and reliable mechanism that is available by default in most operating systems and supported in most kernel versions. AF_PACKET is a good enough option in most cases.
Pros: Widely supported by most OSs and kernel versions, doesn’t require elevated security capabilities.
Cons: Taps only the network interface and not the OS, and no support for XDP. Not as performant as eBPF or PF-RING. Doesn’t provide pod-name/IP resolution, instead has to rely on Kubernetes event-based pod-name/IP resolution.
The AF_PACKET option requires the following security capabilities:
- NET_RAW
- NET_ADMIN
LIBPCAP
How to Use: --set packetCapture=libpcap
In the rare occasions where AF_PACKET isn’t compatible with your OS, the LIBPCAP option can be explicitly set.
LIBPCAP is an older, yet fully functional option for packet capture.
PF-RING, AF_XDP
Kubeshark provides support for additional packet capture methods, however, at this point, using one of these is safe for specific use-cases.
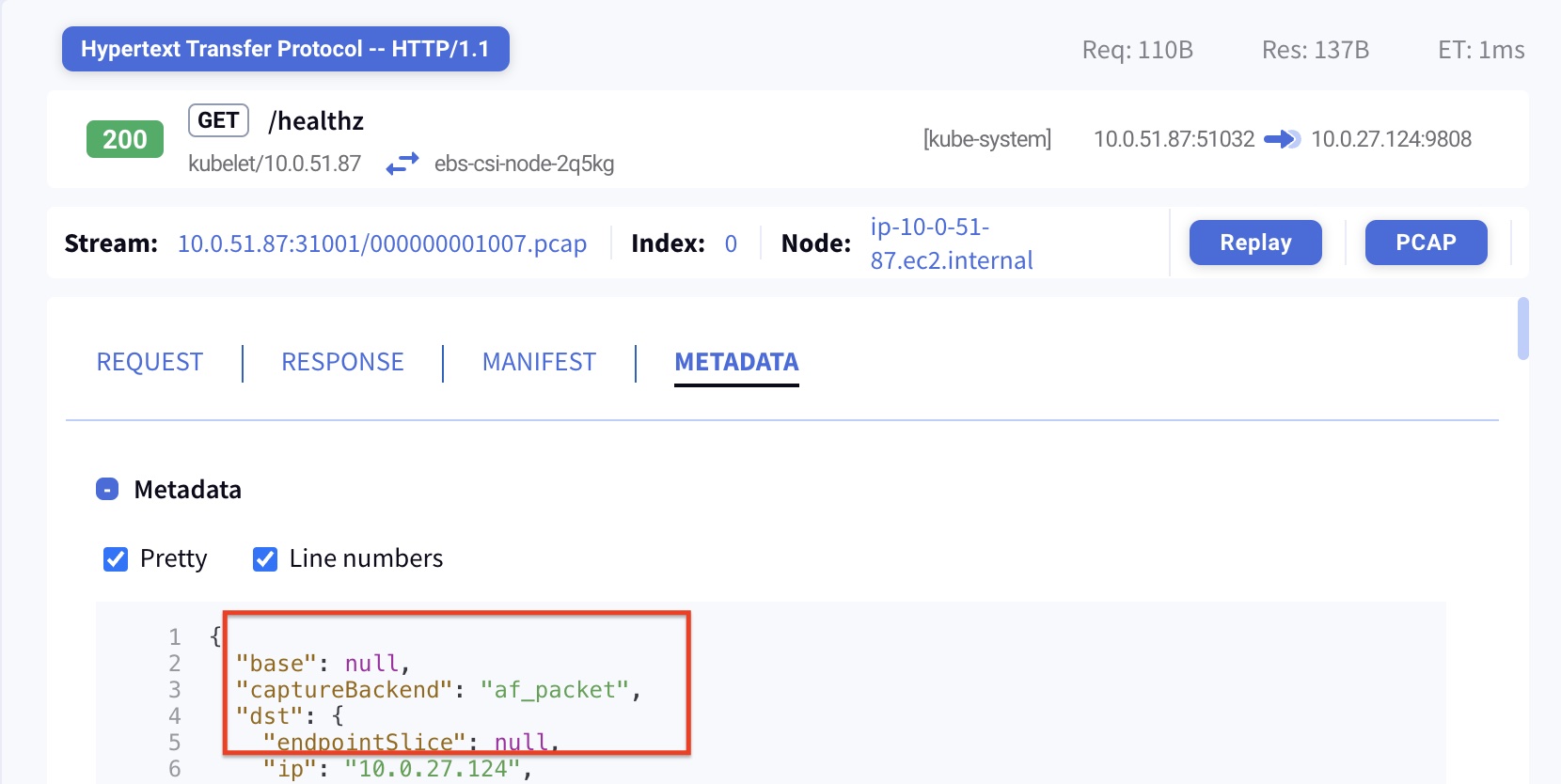
Which Method Was Used
How to learn which packet capture option was used to capture the specific traffic:
The request-response pair metadata includes information related to the packet capture method.
TLS Packet Capture
Kubeshark uses eBPF to intercept TLS traffic. This packet capture option resembles, yet is different from the eBPF traffic capture option mentioned above. This option is enabled by default. Not using this option will disable TLS packet capture. It also uses the same security capabilities. It has wider OS and kernel version support.