Agent Logic
With Network Agents
Users can create and use an unlimited number of Network Agents, each designed to perform a specific network-related automation task.
Agents can detect anomalies and threats, generate reports, export metrics, traces, and logs, enforce network policies, record traffic, and more.
Agent Logic Structure
Each agent’s business logic is written in a JavaScript ES5 script and consists of the following components:
- Hooks – Triggered by specific events in the traffic flow.
- Helpers – Used to invoke integrations and specific Kubeshark functions.
- General Code – Performs calculations and stores information in memory.
Agents process network traffic, perform custom logic, and trigger actions such as generating metrics, exporting logs, producing reports, or automating workflows.
Hooks
Hooks are functions that react to specific network events. They allow the execution of user-defined JavaScript code within Kubeshark’s Golang backend.
For example, the onItemCaptured hook is triggered every time an API call is reassembled. The following example prints the metadata of each captured API call:
function onItemCaptured(data) {
// Print API call metadata
console.log("Msg:", data);
}Hooks run continuously in the background, regardless of whether the dashboard is open or closed.
Common Hooks
| Hook | Triggering Event | Executed On | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
onItemCaptured | When an API call is reassembled | Workers | Triggered for each reassembled message. Useful for quick analysis, calculations, or tagging. |
onHubAction | When hub.action(action, object) is called | Hub | Used for transferring or processing objects in the Hub. |
onPodEvent | On pod events (e.g., restart, crash) | Hub and Workers | Enables response actions like traffic capture before a crash. |
Helpers
Helpers trigger actions and integrations, such as sending messages to Slack or exporting data to AWS. They provide access to Kubeshark’s backend features.
Example: sending data to a webhook:
vendor.webhook(
"POST",
"https://webhook.site/a42ca96d-4984-45dc-8f72-a601448399dc",
JSON.stringify(data)
);Common Helpers
| Helper | Purpose | Executed On | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
console.log | Logging messages | Hub and Workers | Used for debugging or generating custom logs and reports. |
jobs.schedule | Scheduling recurring tasks | Hub and Workers | Runs a function based on a cron expression. Suitable for periodic processing. |
vendor.kinesis.put | Exporting data to AWS Kinesis | Hub and Workers | Sends data to Kinesis for external processing or storage. |
Complete Script Example
This script calculates and logs the number of packets and total traffic (in KB) every minute using the onPacketCaptured hook and a scheduled job:
var packetCount = 0;
var totalKB = 0;
function onPacketCaptured(info) {
packetCount++;
totalKB += info.length / 1000;
}
function logPacketCountTotalBytes() {
console.log("Captured packet count per minute:", packetCount);
console.log("Total KB captured per minute:", totalKB);
packetCount = 0;
totalKB = 0;
}
jobs.schedule("log-packet-count-total-bytes", "0 */1 * * * *", logPacketCountTotalBytes);Script Storage
Scripts are stored in the kubeshark-config-map. They can be developed locally and synced using the kubeshark scripts command, which automatically detects changes.
Scripts must be compliant with JavaScript ES5 and use the
.jsfile extension.
Example:
kubeshark scripts --set scripting.source=/path/to/your/local/folderViewing and Editing Scripts in the Dashboard
All scripts stored in the config map are accessible via the Scripting section in the Kubeshark dashboard:
Script Examples
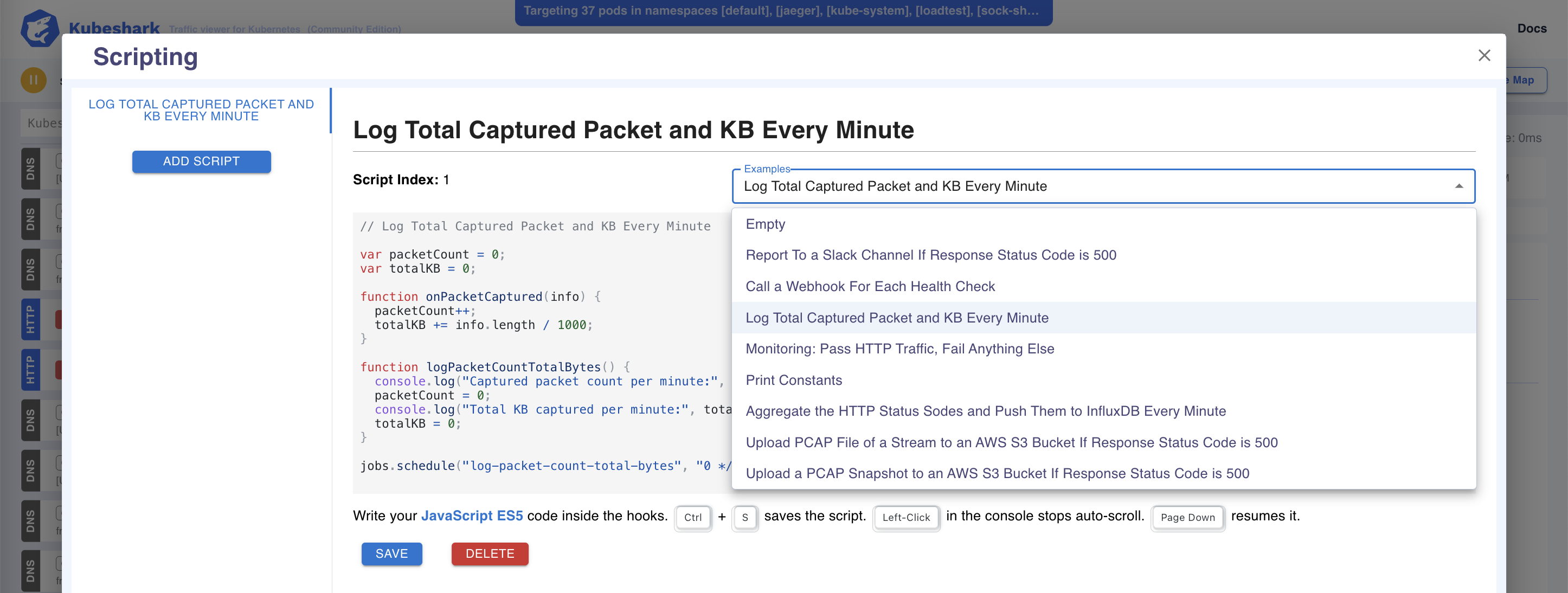
Example scripts are available in the dashboard and can be loaded via the “Examples” dropdown:
Environment Variables
Define script-specific environment variables using the env section in your configuration:
scripting:
env:
SLACK_AUTH_TOKEN: "xo.."
SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: "C0.."
WEBHOOK_URL: "https://webh.."
INFLUXDB_URL: "https://us-e.."
INFLUXDB_TOKEN: "_9r.."
INFLUXDB_MEASUREMENT: "st.."
INFLUXDB_ORGANIZATION: "a.."
INFLUXDB_BUCKET: "al.."Reference these variables in your scripts using the env. prefix:
vendor.influxdb(
env.INFLUXDB_URL,
env.INFLUXDB_TOKEN,
env.INFLUXDB_ORGANIZATION,
env.INFLUXDB_BUCKET,
"Example Measurement", // Measurement name
data, // Payload
{"example": "tag"} // Tags
);Variable Scopes
Kubeshark scripts support the following scopes:
- Function Scope – Defined within a function, accessible only there.
- Script Scope – Defined outside functions, accessible throughout the script.
- Global Scope – Defined using
this, shared across all scripts.