CPU & Memory Consumption
Topics
- Topics
- Resource Consumption
- Kubeshark Operations
- Resource Limitations
- Predictable Consumption
- The Browser
Resource Consumption
Kubeshark’s resource consumption largely depends on the cluster workload and the amount of dissection required. Most resource-consuming operations are performed by the Worker at the node level.
Kubeshark Operations
Kubeshark captures and stores all traffic in memory. It then filters traffic based on pod targeting rules, which include pod regex and a list of namespaces. Traffic filtered out by these rules is discarded. Traffic filtered in is dissected. Among all Kubeshark operations—traffic capturing, storing, filtering, and dissection—dissection is the most resource-intensive and is performed on-demand when a client requests it (e.g., the dashboard, a recording, a running script).
Resource Limitations
While resource consumption can increase based on the amount of traffic targeted for dissection, it can be limited by setting configuration values.
Container Memory and CPU Limitations
Container resources are limited by default. However, allocations can be adjusted in the configuration:
tap:
resources:
hub:
limits:
cpu: 750m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 50Mi
sniffer:
limits:
cpu: 750m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 50Mi
tracer:
limits:
cpu: 750m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 50MiWorker Storage Limitation
Traffic is recorded and stored by the Worker at the Kubernetes node level. Kubeshark generates a PCAP file per L4 stream and a JSON file per API message. Files are deleted based on a TTL:
- PCAP - 10s TTL
- JSON - 5m TTL
If storage exceeds its limit, the pod is evicted. The storage limit is controlled by setting the tap.storagelimit configuration value. To increase this limit, provide a different value (e.g., setting it to 5GB with --set tap.storagelimit=5Gi).
OOMKilled and Evictions
Whenever a container surpasses its memory limit, it will get OOMKilled. If Worker storage surpasses its limitation, the pod will get evicted.
Predictable Consumption
While limitations ensure Kubeshark does not consume resources above set limits, it is insufficient to ensure proper operation if the available resources aren’t adequate for the amount of traffic Kubeshark must process.
To consume fewer resources and not surpass limitations, Kubeshark offers two methods to control the amount of processed traffic:
Capture Filters (Pod Targeting)
Kubeshark allows targeting specific pods using pod regex and a list of namespaces. This ensures only traffic related to targeted pods is processed, and the rest is discarded. Utilizing Pod Targeting can significantly optimize resource consumption:
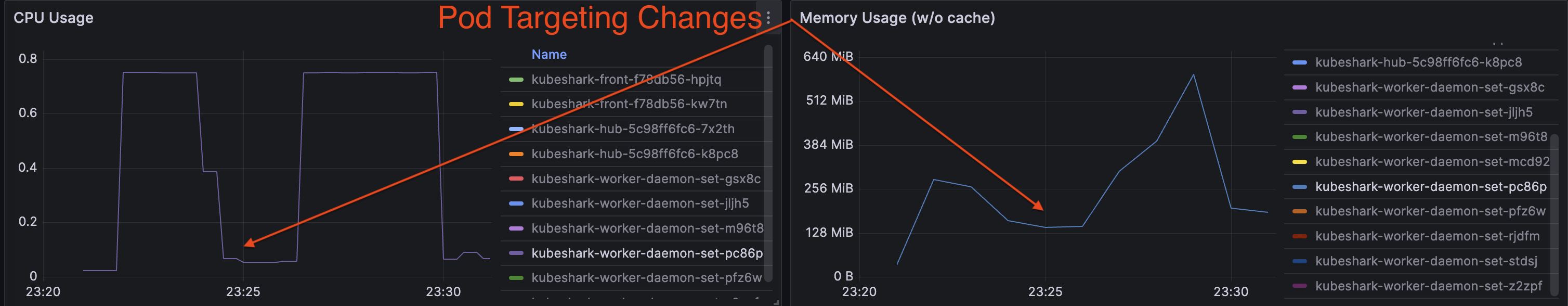
Read more in the Capture Filter section
Traffic Sampling
TrafficSampleRate is a number representing a percentage between 0 and 100. This number causes Kubeshark to randomly select L4 streams, not exceeding the set percentage.
For example, this configuration will cause Kubeshark to process only 20% of traffic, discarding the rest:
tap:
trafficSampleRate: 20The Browser
Be aware that your browser can consume a significant amount of CPU when displaying a substantial amount of traffic.