Capture Filters
Resource consumption (e.g., CPU and memory) is key in Kubernetes. Kubeshark’s resource consumption is linearly dependent on the amount of traffic it processes. There are many ways to control resource consumption, and this Capture Filters feature is one of them.
Capture Filters can help you focus on traffic of interest and avoid processing traffic that isn’t of interest.
Pods in Kubernetes launch and terminate dynamically on nodes scheduled by Kubernetes. To process relevant traffic only, Kubeshark monitors Kubernetes events, especially pod start and termination events, so it can start processing the pods’ traffic when they start on the node they start on. If pods terminate and start elsewhere, Kubeshark will process the traffic for the pod on the new node.
The results per pod of interest are:
- Identifying the node the pod runs on
- Identifying the relevant pod IPs as there can be several (e.g., pod IP, service IP, multi-NIC IP, etc.)
- Capturing traffic on the target node related to the target IPs
- Processing captured traffic
Pod Targeting
Pod Targeting enables the targeting of specific pods using pod regex (regular expression) and a list of namespaces. It monitors Kubernetes events to track pods that match these criteria across nodes and replicas, tapping into their traffic from launch until termination.
Namespace Targeting
Kubeshark will monitor Kubernetes events and process traffic for all pods that are part of the target namespaces across all nodes in the cluster.
Excluding Namespaces
The opposite operation to targeting namespaces is excluding namespaces. Explicitly ignore traffic from pods that are part of the excluded namespaces list.
Explicit BPF Expression (Traffic Targeting)
Another way to target specific traffic is by using an explicit BPF expression written in BPF syntax. This BPF expression will be used to target traffic, and any Pod Targeting rules will be ignored. Examples of BPF expressions include: net 10.10.0.0/16 or host 12.13.14.15.
Setting an explicit BPF expression that overrides other rules is available only when AF_PACKET is used as a packet capture library. Read here to learn how to explicitly set AF_PACKET as the packet capture library.
Dynamically Changing The Traffic Targeting Rules
You can dynamically set the Pod Targeting properties and the BPF expression from the dashboard. To operate the Pod Targeting dialog window, press the kube button located to the right of the Pod Targeting section.

In the dialog window, you can set the namespaces and the pod regex:

The following video demonstrates the behavior:
Processing Traffic Consumes CPU and Memory
Kubeshark’s resource consumption is directly related to the amount of traffic it processes. This becomes a significant issue in busy clusters. Limiting CPU and memory consumption doesn’t guarantee efficient operation if the allocated resources are insufficient for the traffic volume that Kubeshark needs to handle.
Moreover, the dynamic and distributed architecture of Kubernetes can lead to challenges in tracking and tapping targeted pods, as pods may start and stop, have replicas, and move across nodes.
These Grafana panels show the implications on CPU and memory consumption:
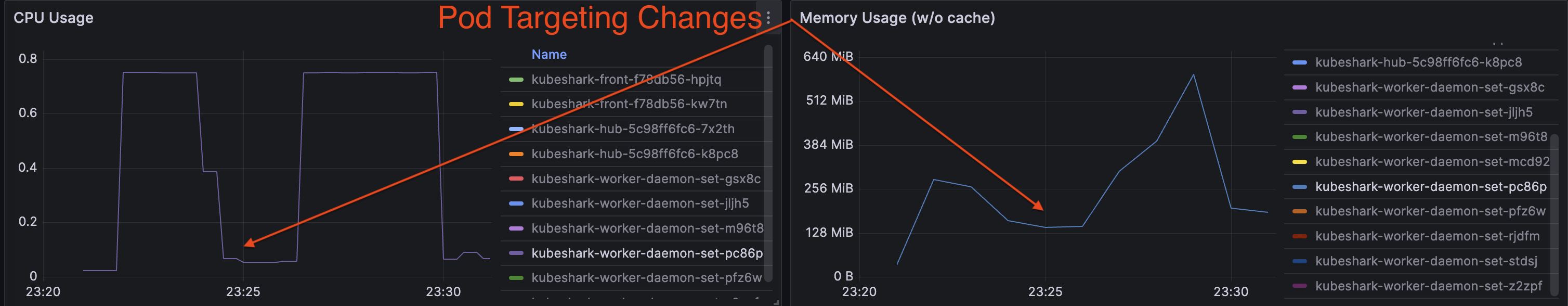
Starting with Default Traffic Targeting Rules
Default rules can be set in the configuration (e.g., values.yaml). For instance, the following configuration directs Kubeshark to process only traffic associated with pods matching the regex catal.* in the ks-load or sock-shop namespaces:
tap:
regex: catal.*
namespaces:
- ks-load
- sock-shop
excludeNamespaces:
- kube-systemSetting a BPF expression will override any existing Pod Targeting rules.
tap:
regex: catal.*
namespaces:
- ks-load
- sock-shop
bpfOverride: net 10.10.0.0/16KFL vs. Traffic Targeting (Display vs. Capture Filters)
KFL should not be confused with Traffic Targeting as they serve different purposes. KFL statements only affect the data presented in the Dashboard, whereas Traffic Targeting determines which pods are targeted and, consequently, which traffic is tapped.
For those familiar with Wireshark, KFL can be likened to Wireshark’s Display Filters, and Traffic Targeting to Wireshark’s BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) filters.